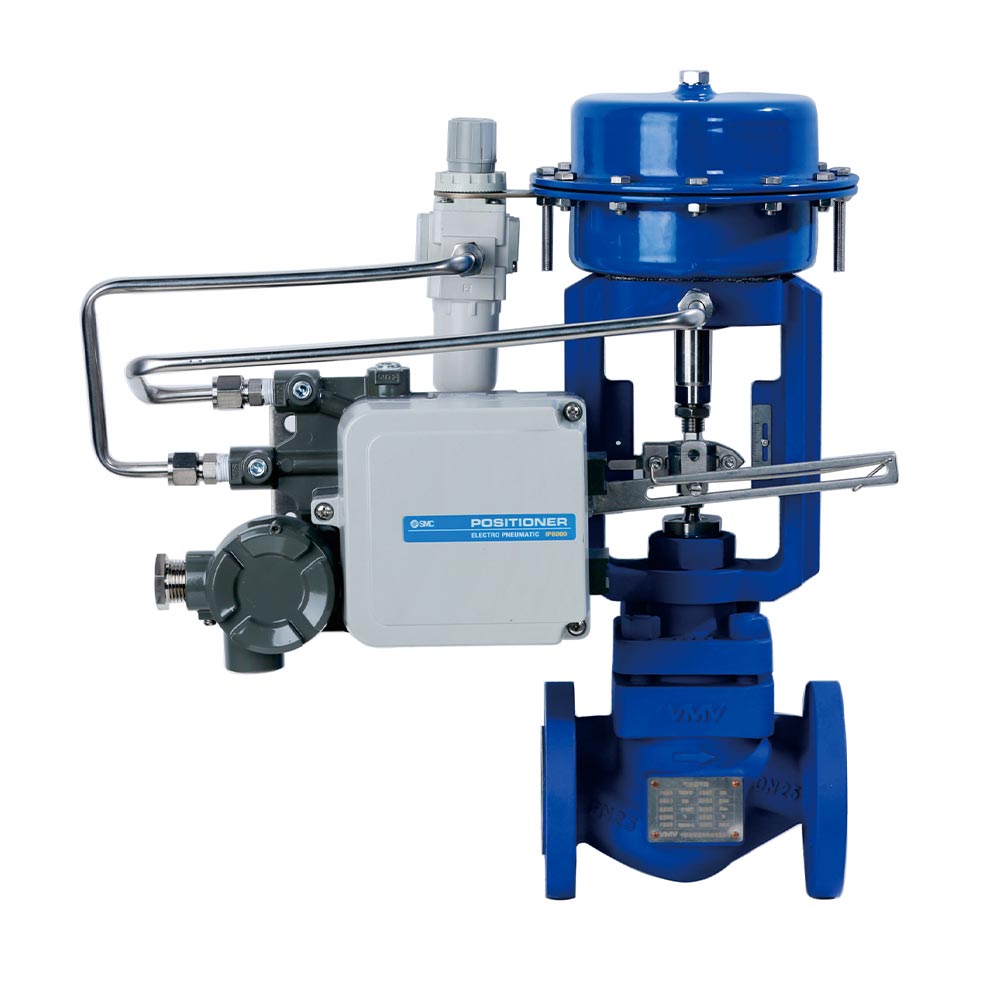
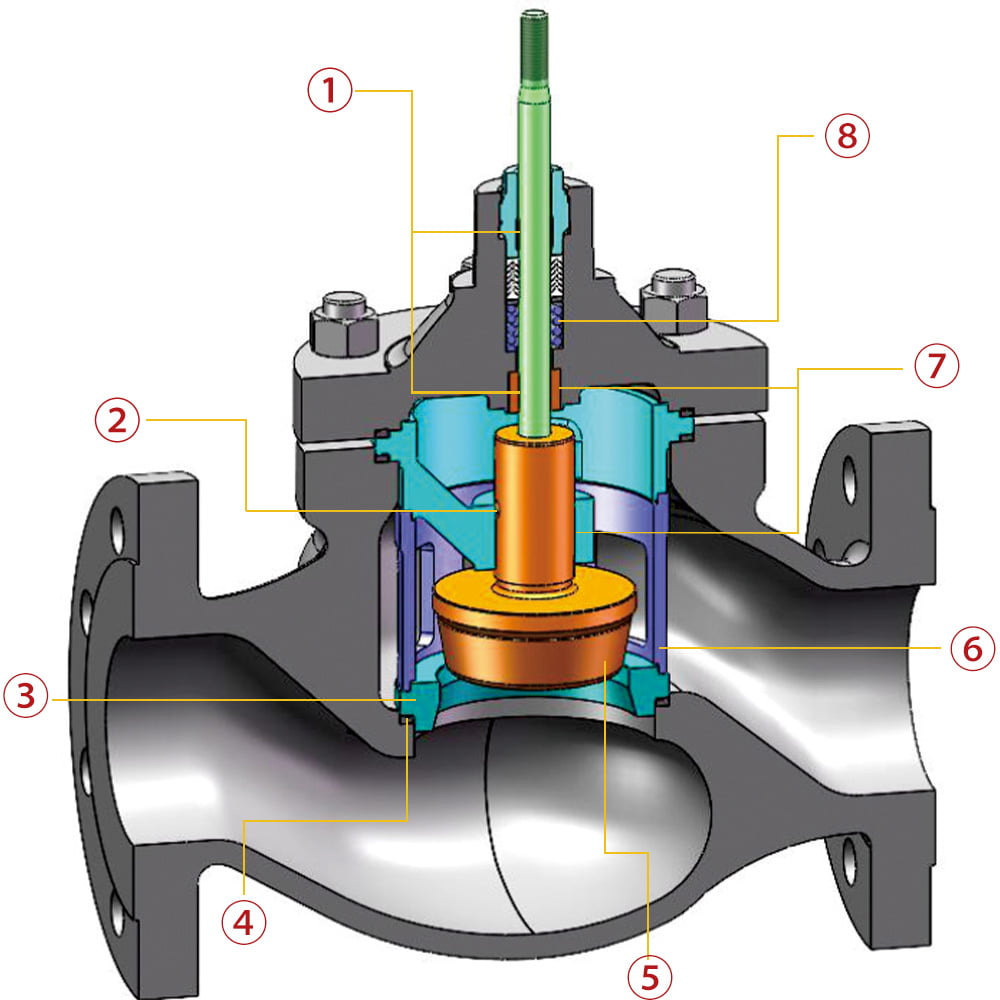
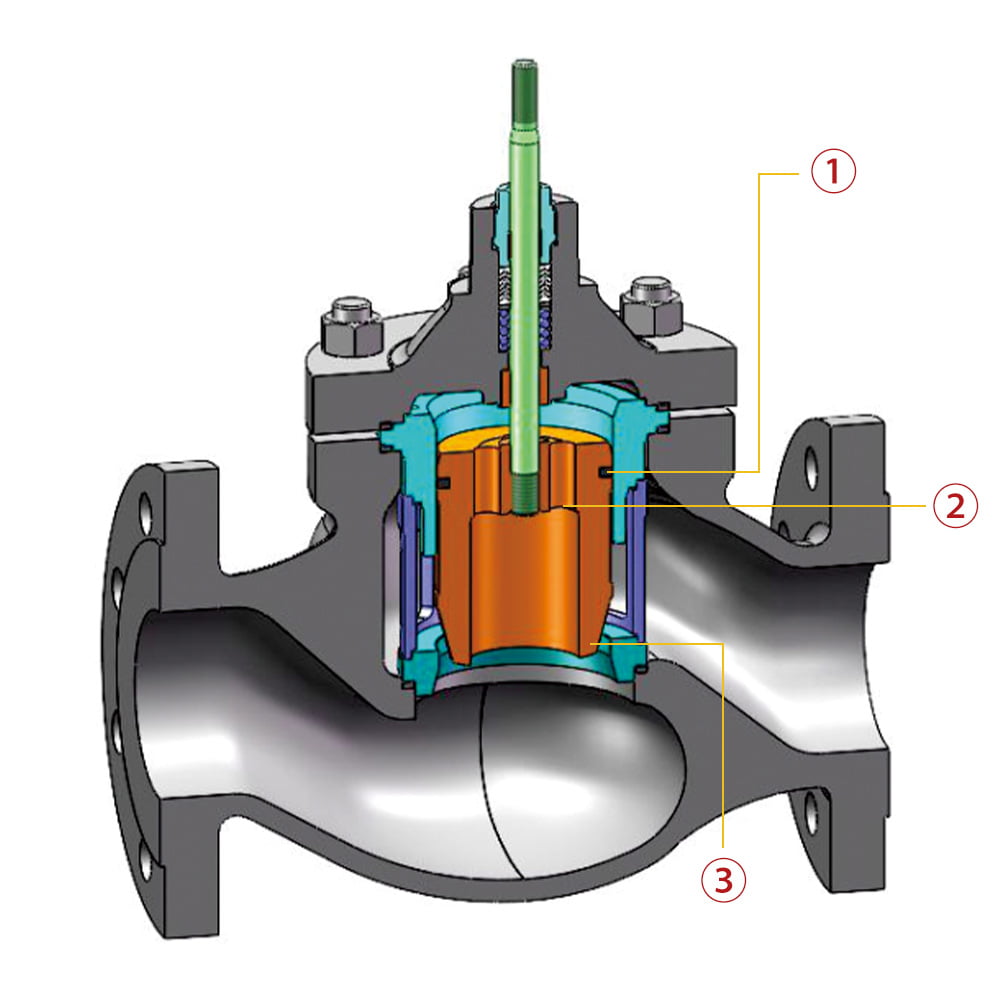
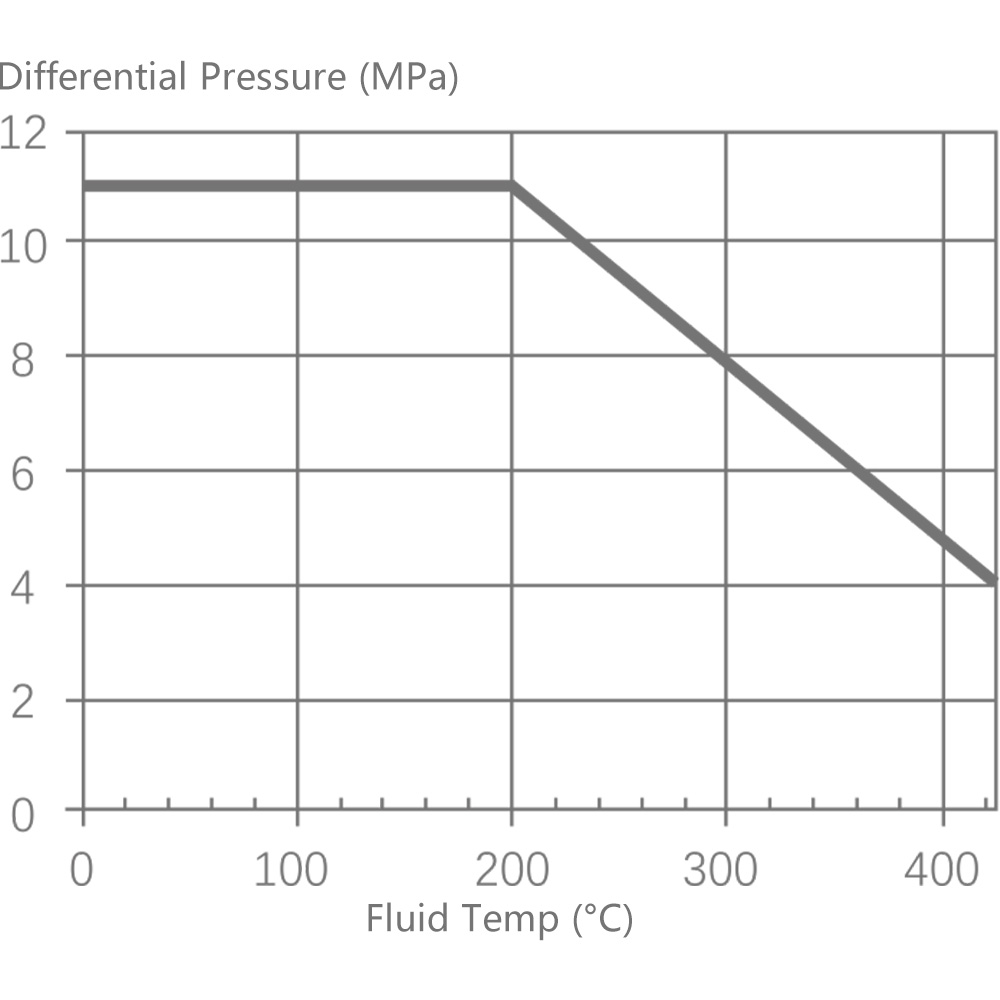
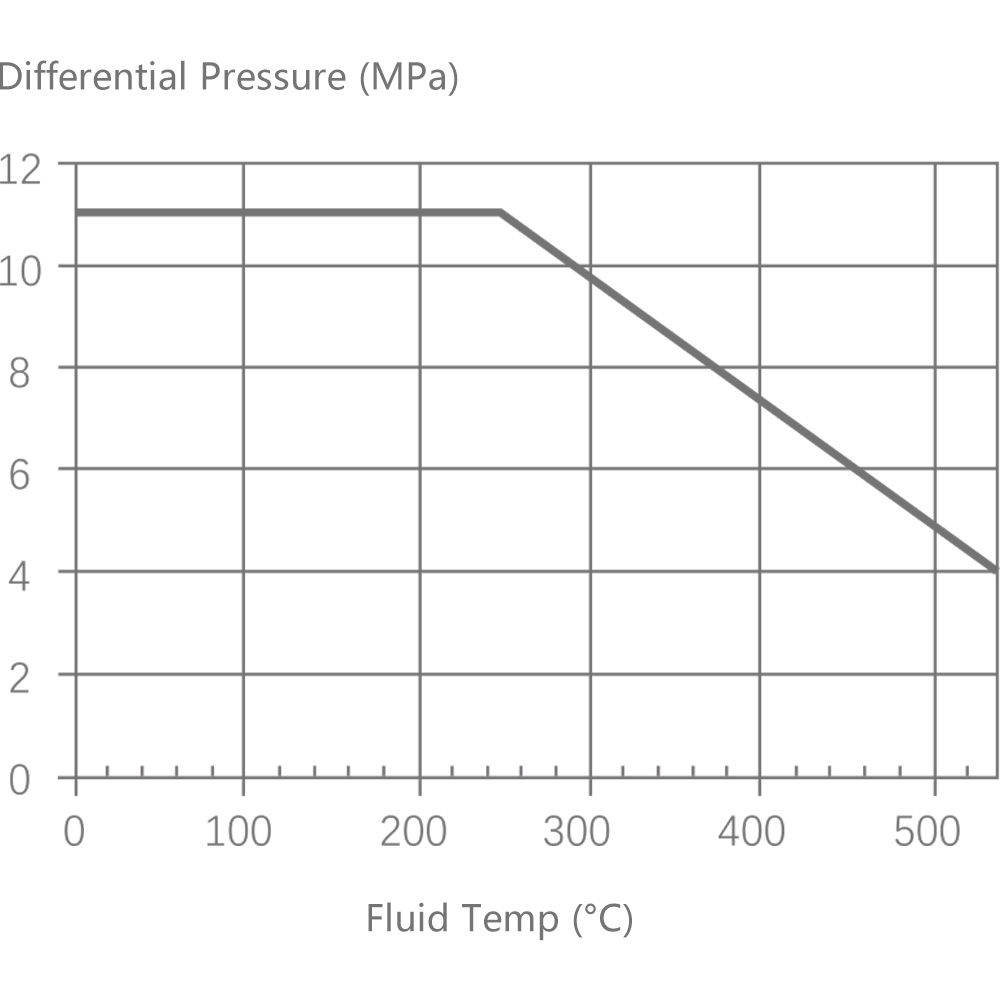
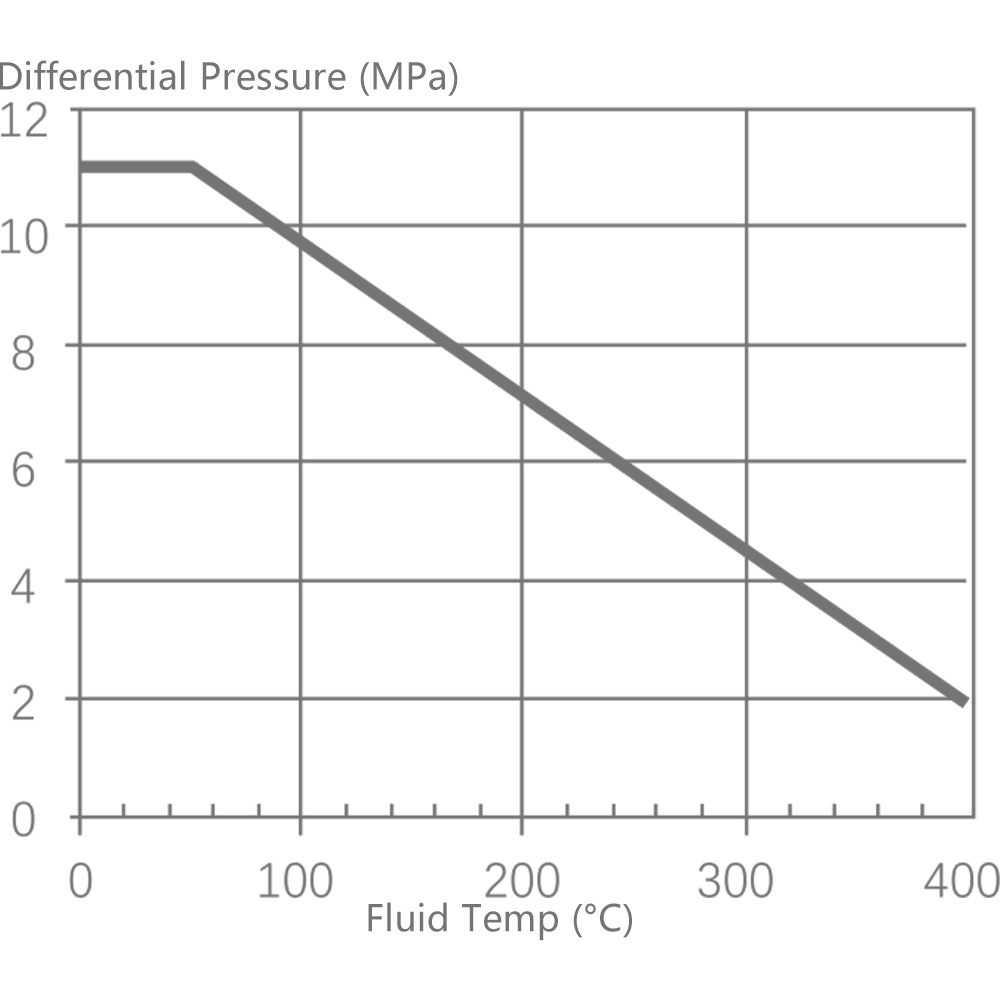
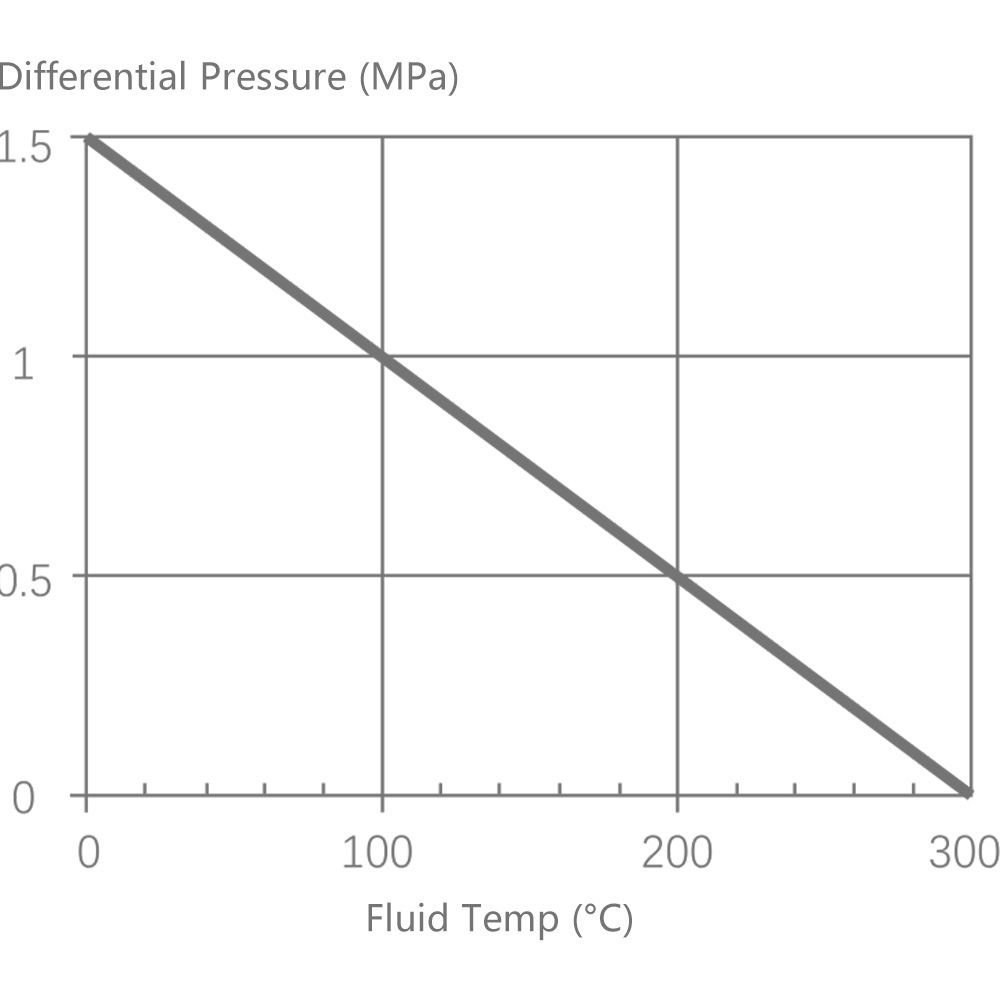
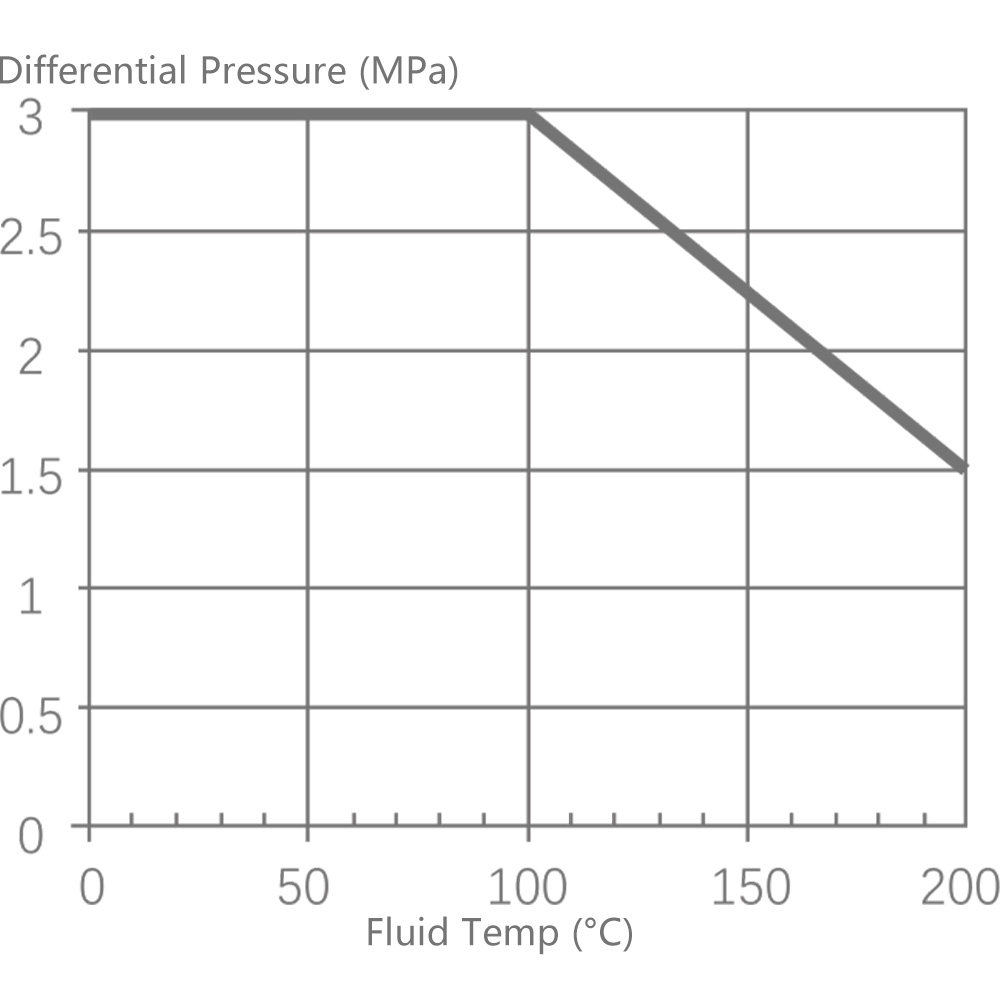
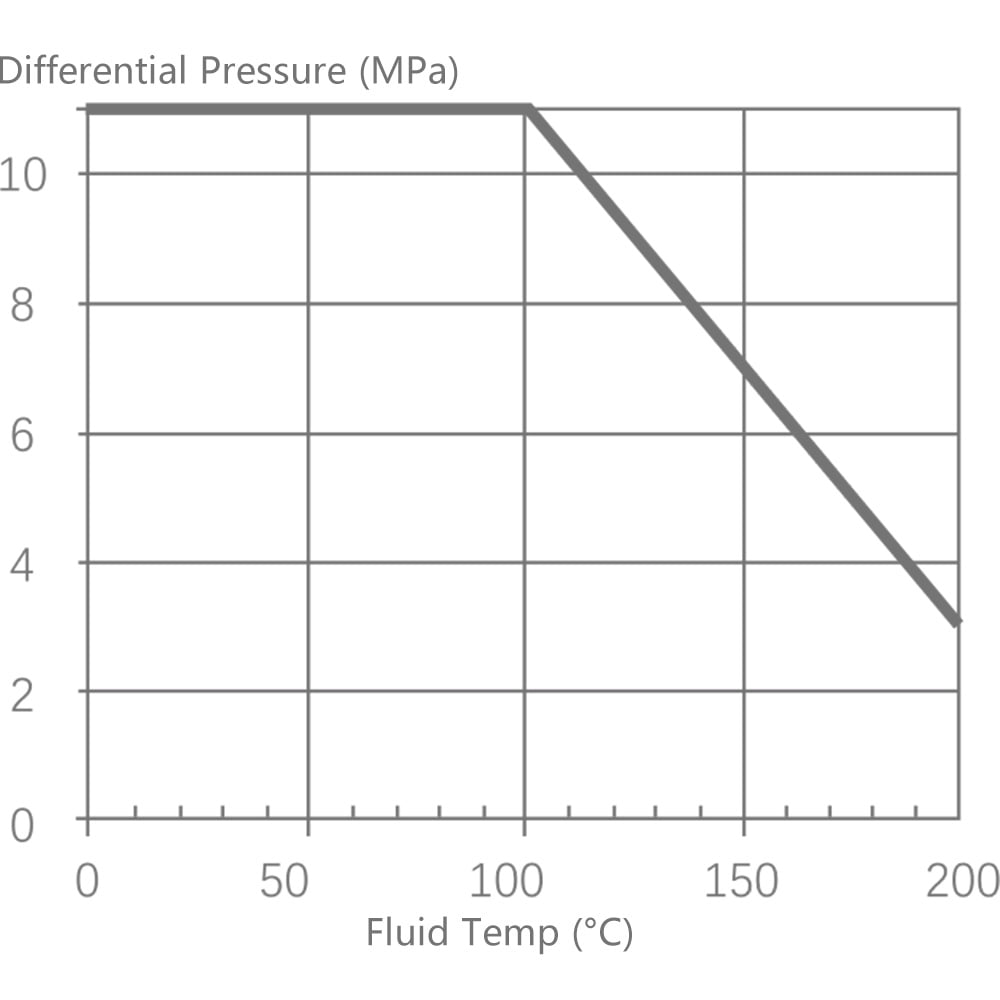
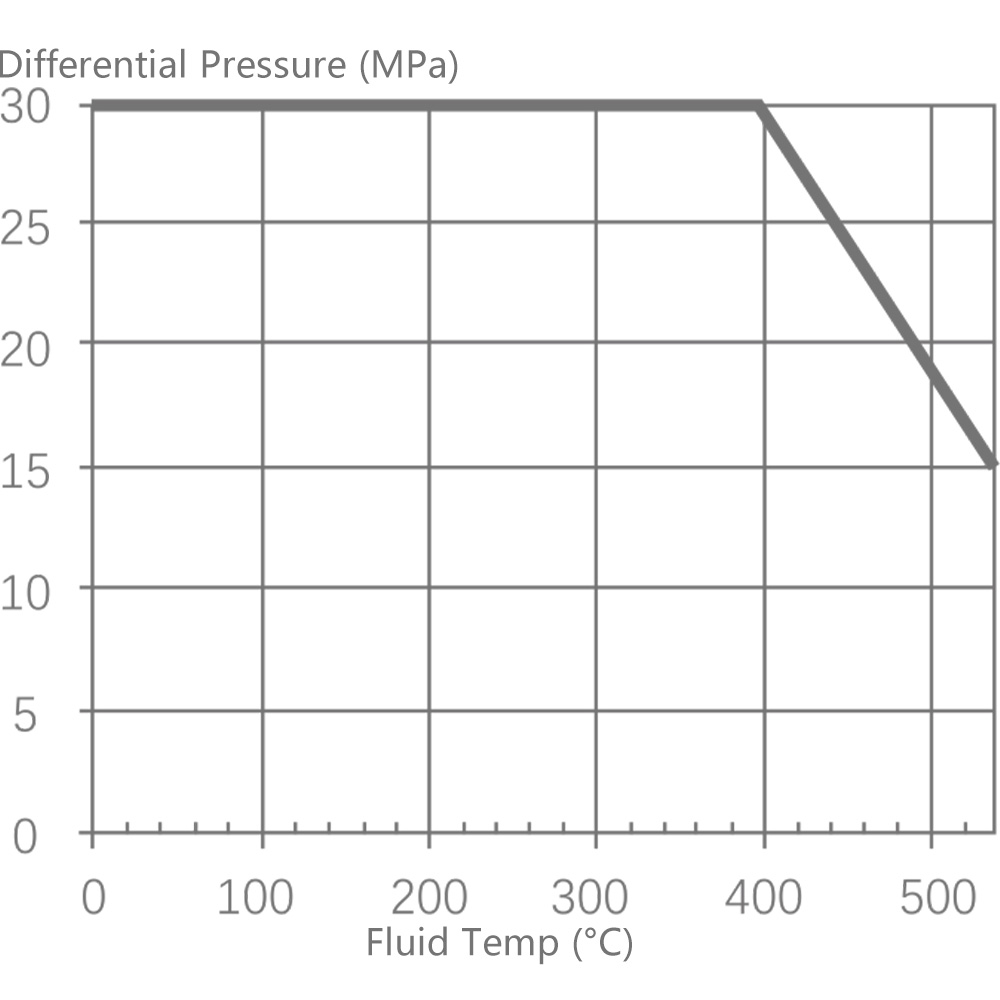
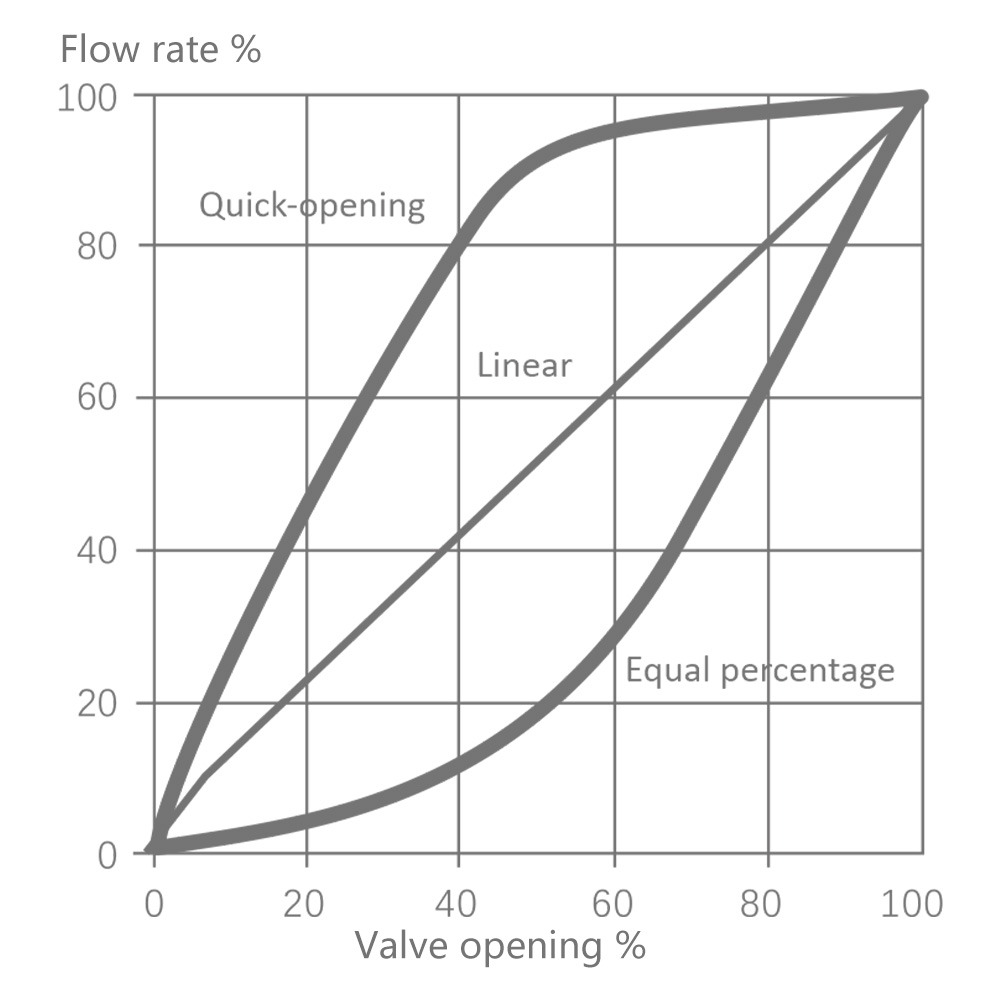
6.1 Single-seat control valve

①. Valve stem double guided structure
Keeping the packing and valve stem coaxial at any times can prevent abnormal wear of the packing caused by eccentricity,greatly improving the service life of the packing.
②. Thread + pin connection structure
The valve plug and the valve stem is lightly connected by threads and pins, with no any relative movement gap, effectively prevent fatigue and fracture of the valve stem from relative swing of the valve plug and valve stem.
③. Up-pressure valve seat structure
By loosening the valve bonnet bolts, the internal components of the valve can be removed one by one, allowing for quick maintenance and components onsite, thus saving the user’s replacement of the valve seat and internal maintenance time.
④. Gasket quantitative compression structure
Prevent the gasket from being overly compressed to achieve durable sealing without external leakage.
⑤. Single seat sealing structure
Lower leakage and hard sealing can meet level V and above leakage requirements for a long time.
⑥. Elastic pressure cage compensation structure
Under high-temperature conditions, the pressure cage can absorb the axial displacement caused by high temperatures and convert it into radial elastic deformation, prevent the gasket or valve internal components from failing due to thermal stress deformation.
⑦. Valve plug double-guided structure
The valve plug operates smoothly, not prone to vibriaon and sticking, ensuring higher regulating precision.
⑧. Spring-loaded packing gland structure
Provide a continuous and stable compressive force for the packing, allowing the packing to automatically compensate for wear during use, achieving long-term stable sealing.
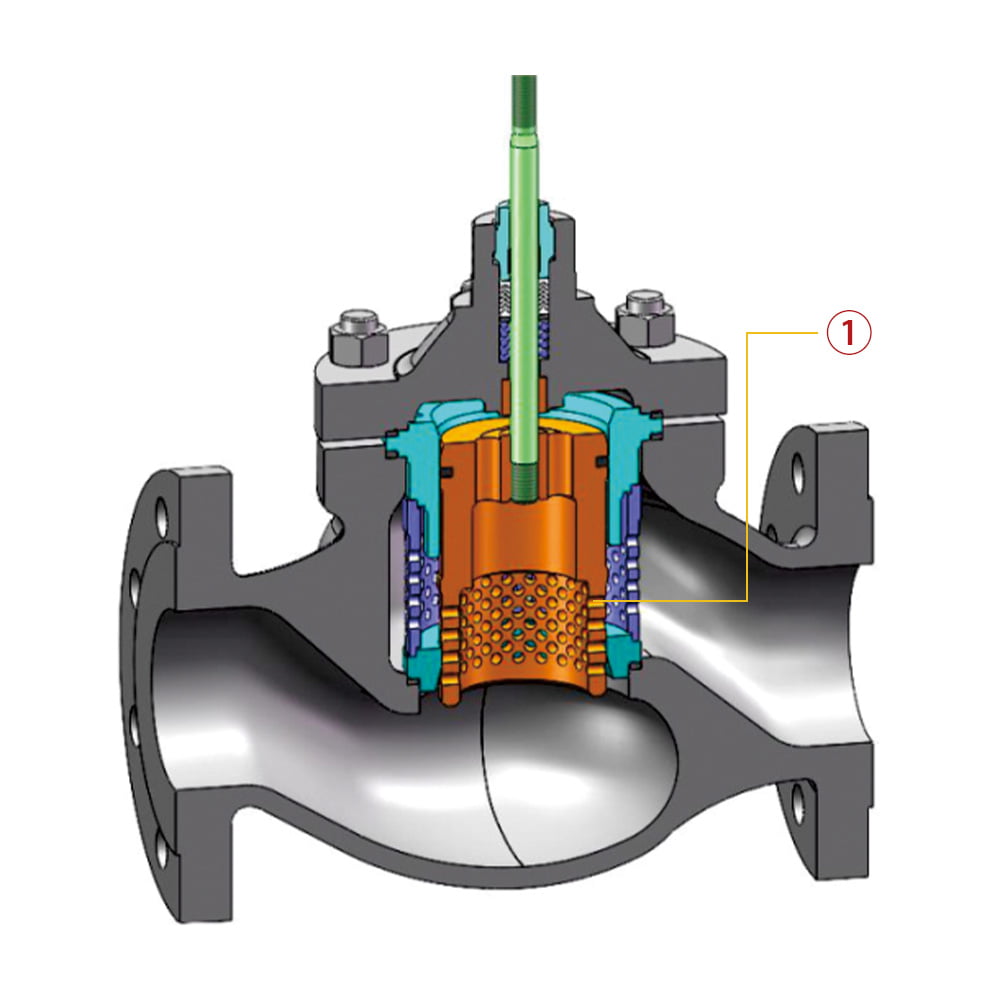
6.2 Balanced single-seat control valve

①. Wear-resistant piston ring seal structure
The wear-resistant piston ring still has self-lubricating at temperatures above 200°C, making the valve not easy to stretch and block during the long period
regulating process, maintaining a seal grade above level IV .
②. Balanced single seat structure
Low thrust overcomes the large pressure difference, has better performance of
overcoming differential pressure.
③. Spherical valve plug structure
The throttling orifice is uniformly distributed on the valve plug, allowing the medium to flow smoothly and stably, thus achieving higher regulating precision.
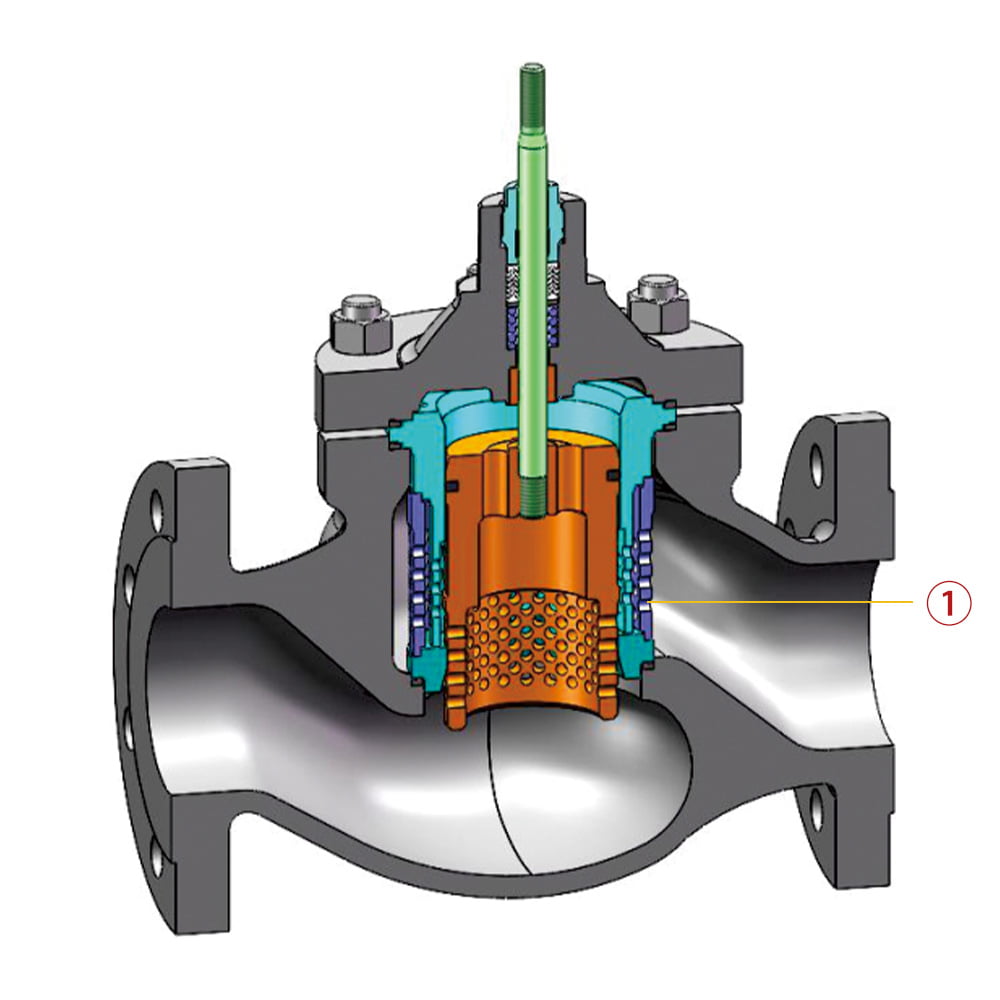
6.3 Low noise control valve

①. Low noise valve plug structure
This design reduces the flow speed of the medium, thus diminishing the erosion of the valve plug and seat caused by high flow speed, increasing its service life.
It also lowers noise, reducing environmental noise pollution.
Decreased vibrations, prevent damage to valve internal components from high-frequency vibrations, enhancing regulating precision and service life.
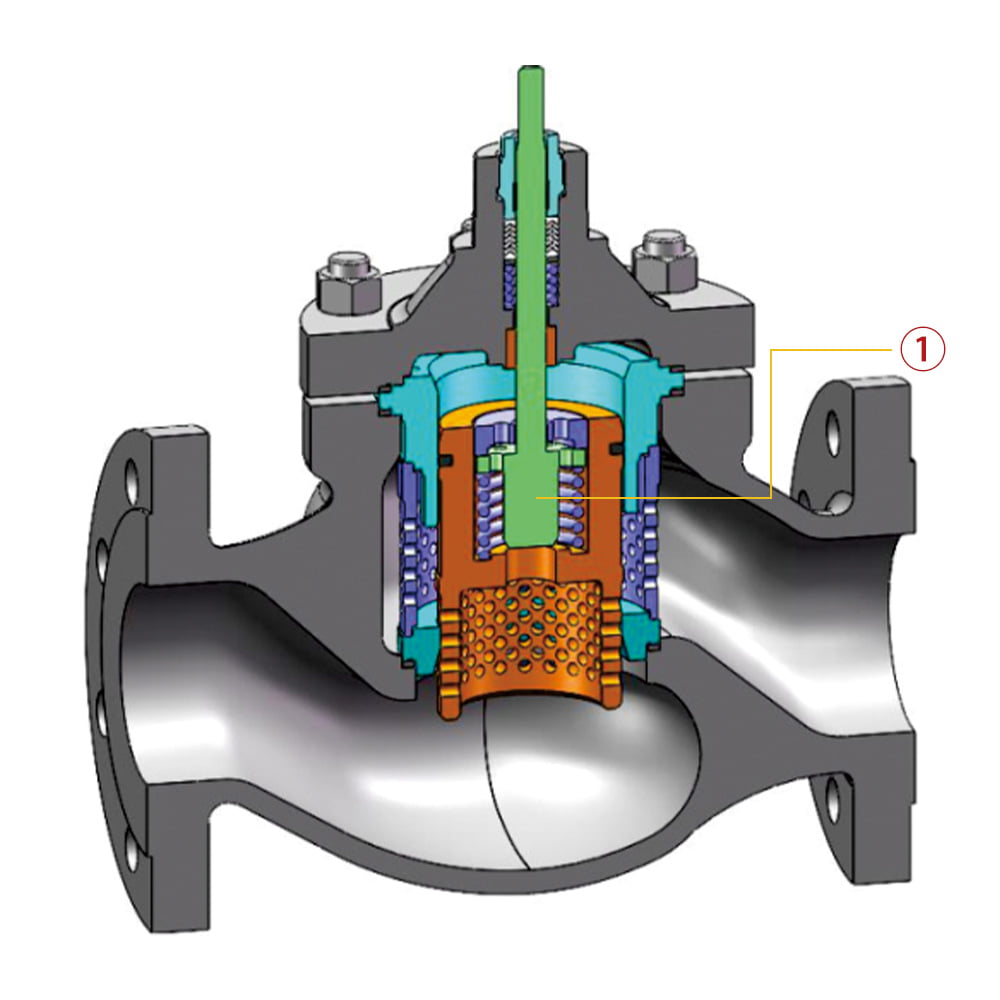
6.4 Multi-stage pressure reducing control valve

①. Multi-stage pressure + reducing valve plug structure
Used in conditions with high differential pressure to reduce medium flow speed and minimize the erosion to the valve plug and seat that occurs at high speed, thereby prolonging the valve’s service life.
It also reduces noise, lessening noise pollution to the environment.
The structure also diminishes vibrations, preventing damage to valve internal components due to high-frequency vibrations and improving the precision of regulation as well as service life.
6.5 Pilot control Valve

①. Pilot operated valve plug structure
Equipped with regulating and shutoff function, it has excellent sealing
performance under high temperature (>230 ℃) working conditions and can ensure long-term operation with sealing above level V.
The structure also diminishes vibrations, preventing damage to valve components due to highfrequency vibrations and improving the precision of regulation as well as service life.